Displaying 11 - 20 of 191
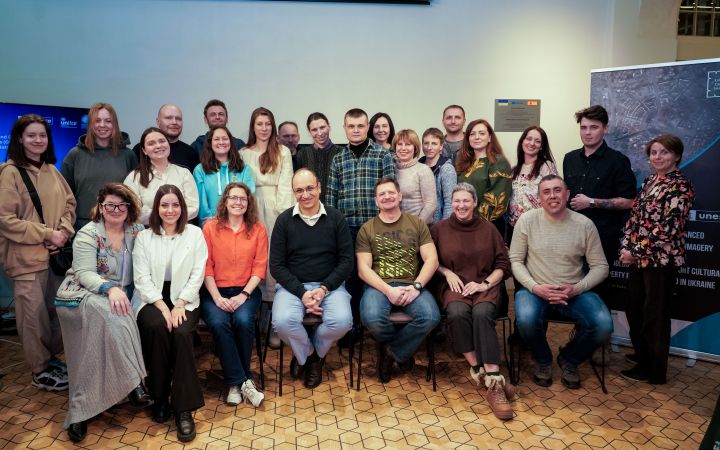
28 February 2025, Lviv, Ukraine – In a significant step toward safeguarding Ukraine’s cultural and natural heritage, UNOSAT and UNESCO hosted an advanced training session in Lviv from 25-28 February 2025. With a focus on satellite imagery-based damage assessment and environmental monitoring, Ukrainian heritage professionals and archaeologists honed their skills in geospatial technologies. Through hands-on exercises and open-source platforms, participants learned to document and monitor invaluable heritage sites—empowering them to make a real impact in their daily work. This training is part of an ongoing effort to bolster Ukraine’s capacity to preserve its rich cultural legacy and natural heritage in the face of ongoing challenges.
22 February 2025, Geneva, Switzerland – The United Nations Institute for Training and Research (UNITAR) is pleased to announce that Michelle Gyles-McDonnough has officially assumed office as its new Executive Director. She succeeds Nikhil Seth of India, whose mandate concluded on 31 January 2025.
16 December 2024, New York, USA - United Nations Secretary-General António Guterres announced today the appointment of Michelle Gyles-McDonnough of Jamaica as the new Executive Director of the United Nations Institute for Training and Research (UNITAR). She will officially assume her duties on 22 February 2025, succeeding Nikhil Seth of India, to whom the Secretary-General expressed profound gratitude for his dedication and contributions to the United Nations.
24 October 2024, In September, Member States came together to adopt a visionary Pact for the Future aimed at aligning international efforts with contemporary realities and future challenges. Today, on UN Day, the six research and training institutes of the United Nations reaffirm their commitment to supporting the Pact of the Future through specialized knowledge, learning, research and training for the UN system – benefitting the world as a whole.
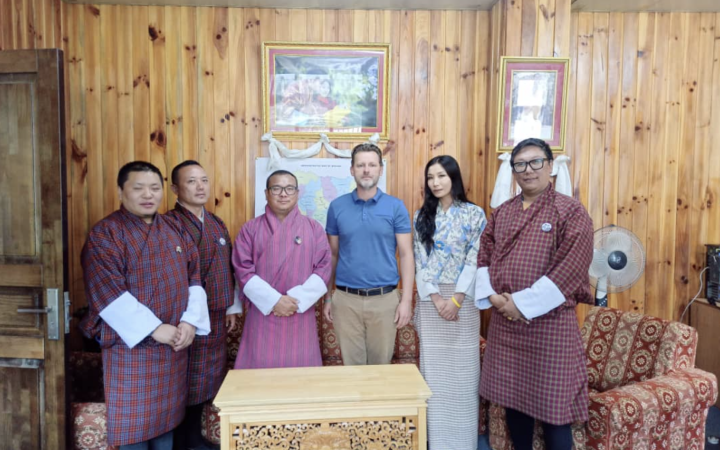
22 October 2024, Geneva, Switzerland - Nestled in the Eastern Himalayas, Bhutan is a country known for its breathtaking landscapes and mountainous terrain. However, this landlocked nation faces significant environmental challenges. As one of the most climate-vulnerable countries in the world, Bhutan’s fragile ecosystem, with around 2,700 glaciers, is increasingly impacted by global warming. Melting glaciers have led to increased risks of floods, landslides, and other natural disasters, threatening communities and ecosystems.
In response to these challenges, the United Nations Satellite Centre (UNOSAT), in collaboration with Bhutan’s government, has focused on enhancing the country’s resilience through the use of advanced geospatial information technologies (GIT). By strengthening local capacities, UNOSAT plays a pivotal role in supporting Bhutan’s efforts to address climate vulnerability and improve disaster risk management.
In response to these challenges, the United Nations Satellite Centre (UNOSAT), in collaboration with Bhutan’s government, has focused on enhancing the country’s resilience through the use of advanced geospatial information technologies (GIT). By strengthening local capacities, UNOSAT plays a pivotal role in supporting Bhutan’s efforts to address climate vulnerability and improve disaster risk management.
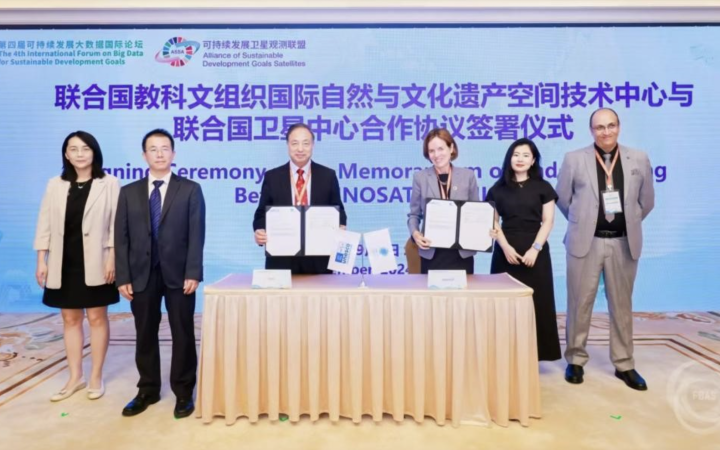
A Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) was signed on September 6, 2024, between the International Centre on Space Technologies for Natural and Cultural Heritage (HIST) under the auspices of UNESCO and the United Nations Satellite Centre (UNOSAT). The agreement was formalized during the 4th Forum on Earth Observation for Sustainable Development Goals, signaling a major advancement in the use of space technology for the protection of World Heritage sites.
Micky Welin's journey in disaster risk management (DRM) showcases the power of education and collaboration in enhancing disaster preparedness and response. Working as the Planning and Logistics Support Officer at Vanuatu's National Disaster Management Office (NDMO), Micky recognised the crucial need for advanced skills in Geospatial Information Technology (GIT) for effective disaster management.
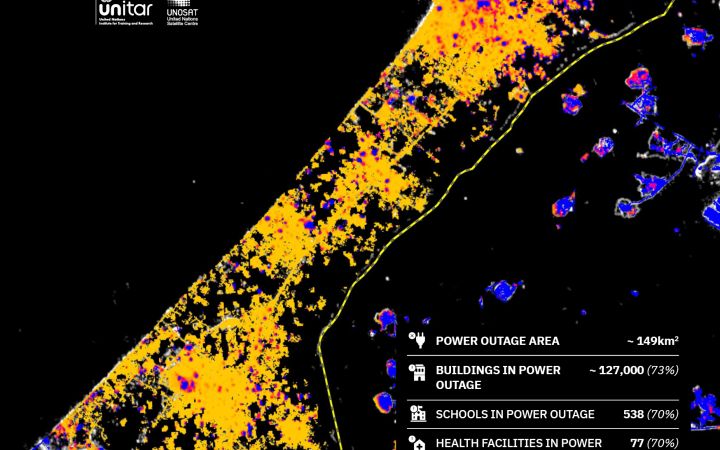
The increase in disaster occurrences and the high numbers of victims resulting from conflicts are urgent issues that require effective and rapid action. Satellite imagery analysis is a vital tool essential in this response, as it can cover large areas and provide accurate information in near real-time.
UNOSAT’s Emergency Mapping Service (EMS), funded by the Norwegian Ministry of Foreign Affairs (NMFA), provides satellite image analysis during humanitarian emergencies related to disasters, complex emergencies and conflict situations. With a 24/7 year-round availability to process requests, the team of experienced analysts ensure timely and tailored delivery of satellite imagery-derived maps (both web and static maps), reports and data ready for direct inclusion in Geographic Information Systems (GIS) for evidence-based decision-making and operational planning.
UNOSAT’s Emergency Mapping Service (EMS), funded by the Norwegian Ministry of Foreign Affairs (NMFA), provides satellite image analysis during humanitarian emergencies related to disasters, complex emergencies and conflict situations. With a 24/7 year-round availability to process requests, the team of experienced analysts ensure timely and tailored delivery of satellite imagery-derived maps (both web and static maps), reports and data ready for direct inclusion in Geographic Information Systems (GIS) for evidence-based decision-making and operational planning.
The increase in disaster occurrences and the high numbers of victims resulting from conflicts are urgent issues that require effective and rapid action. Satellite imagery analysis is a vital tool essential in this response, as it can cover large areas and provide accurate information in near real time.
UNOSAT’s Emergency Mapping Service (EMS), funded by the Norwegian Ministry of Foreign Affairs (NMFA), provides satellite image analysis during humanitarian emergencies related to disasters, complex emergencies and conflict situations. With a 24/7 year-round availability to process requests, the team of experienced analysts ensure timely and tailored delivery of satellite imagery derived maps (both web and static maps), reports and data ready for direct inclusion in Geographic Information Systems (GIS) for evidence based decision making and operational planning.
UNOSAT’s Emergency Mapping Service (EMS), funded by the Norwegian Ministry of Foreign Affairs (NMFA), provides satellite image analysis during humanitarian emergencies related to disasters, complex emergencies and conflict situations. With a 24/7 year-round availability to process requests, the team of experienced analysts ensure timely and tailored delivery of satellite imagery derived maps (both web and static maps), reports and data ready for direct inclusion in Geographic Information Systems (GIS) for evidence based decision making and operational planning.
1 August 2024, Geneva, Switzerland,– The recent conflict in the Gaza Strip has produced a volume of debris that is 14 times greater than the combined total from all conflicts over the past 16 years. This finding comes from a comprehensive assessment conducted by UN-HABITAT and UNEP. The analysis, using satellite imagery analysis provided by UNOSAT, offers a detailed view of the extensive destruction and its implications for debris management.