Displaying 91 - 100 of 179
19 February 2021, Geneva, Switzerland - UNITAR/UN CC:Learn and MIET Africa are turning climate change into an everyday topic in Malawi, Zambia and Zimbabwe. Through a series of TV and radio programs, the two projects are streamlining the access to climate change discussions and raising awareness of this issue among people who previously didn't have a chance to get any information about it.
19 February 2021, Geneva, Switzerland - The Green Development and Climate Change Programme and the Multilateral Diplomacy Division joined forces to deliver the Online Training Programme on Climate Change Diplomacy, at which 35 Kenyan diplomats, government officials, and civil society representatives were trained on climate diplomacy. The training took place between 13 November and 8 December 2020 and provided participants with knowledge on climate change and climate diplomacy, building their capacity for the upcoming climate negotiations at COP 26.
11-14 January 2021, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia – A group of 97 senior officials and ambassadors from the Ministry of Foreign Affairs and the Ministry of Environment, Forest, and Climate Change engaged in a four-day UNITAR High-Level e-Workshop to improve their skills and knowledge in environmental diplomacy, in the lead-up to this year’s Conference of Parties (COP26). The activity was made possible with the financial support of SIDA, Sweden’s government agency for development cooperation.
12 February 2021, Georgetown, Guyana - UNITAR through the Partnership for Action on Green Economy co-organized a workshop on 'Building back better through trade and industrial policy' in Guyana. The workshop aimed at building technical knowledge and skills related to the design, implementation, and evaluation of public policy at the trade and industry interface, thus supporting local agents in the achievement of national sustainable goals.
3 February 2021, New York, USA (Virtual) – The United Nations Institute for Training and Research (UNITAR) New York office announced the launching of “Harnessing Climate & SDG Synergies to Raise Ambition in the Era of Paris+5 and Pandemic Recovery” an online course series in collaboration with the United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs (UNDESA) and United Nations framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCC).
"We were stranded in the school, unable to move anywhere because the streets were submerged, and many people lost their lives. It is caused by Coral abstraction and cutting mangroves, but climate change is making the problem even worse".
20 January 2021, Geneva, Switzerland – UNOSAT delivered a four week e-learning moderated course under the framework “Strengthening Women’s Disaster Management Capacities in Guyana and Dominica”, a project funded by the Government of Japan and led by UNDP Guyana. The e-learning event is part of the capacity development activities planned under the second component of the “Development of Guyana’s National Flood Early Warning System (NFEWS)" initiative.
UNITAR and UN CC:Learn joined forces to deliver the Online Training Programme on Climate Change Diplomacy, at which 35 Kenyan diplomats, government officials, and civil society representatives were trained on climate diplomacy. The training took place between 13 November and 8 December 2020 and provided participants with knowledge on climate change and climate diplomacy, building their capacity for the upcoming climate negotiations at COP 26.
26 November 2020, Geneva, Switzerland - Following the signing of a Memorandum of Understanding, UNITAR and the International Ocean Institute launched the Online Diploma on Ocean Governance for Sustainable Marine Ecosystems.
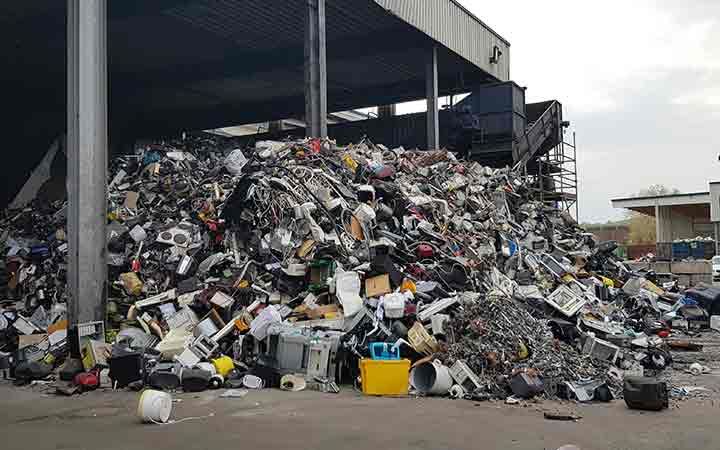
24 November 2020, Bonn, Germany - UNITAR/United Nations University present an in-depth review on the WEEE Collection Rates in the EU-28, Switzerland, Norway and Iceland, which shows that the implementation mechanisms of WEEE legislation, such as the ‘all actors’ approach, a clearing house, and mandatory handover positively contribute to WEEE collection. In 2018, 55% of WEEE has been reported and collected to the WEEE Directive, at least 20% of WEEE has been traced to be in other WEEE Flows, such as illegal exports of WEEE, exports for reuse, mixed with metal scrap and in residual solid waste. The whereabouts to 25% of the WEEE is still unknown.